Enhancing Cancer Care Through Specialized Expertise
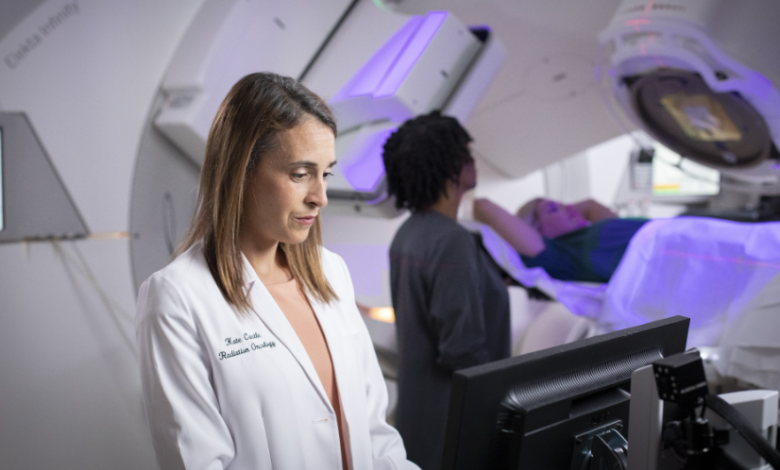

The Role of Medical Oncologists
A medical oncologist plays a vital role in the comprehensive care of patients diagnosed with cancer. These specialists focus on evaluating, diagnosing, and managing various forms of cancer using evidence-based treatments. Their expertise extends from designing treatment plans to coordinating care with surgeons, radiation oncologists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure a holistic approach.
Common Types of Cancer Managed
Patients often consult a medical oncologist for diverse forms of cancer, including breast, lung, colorectal, blood cancers, and rare malignancies. Early detection and tailored treatment plans are crucial in improving patient outcomes. Medical oncologists also monitor disease progression and adjust therapies as needed to maintain the effectiveness of care.
See also: How Residential Cleaning Services Help Maintain a Healthier Living Space
Diagnostic Procedures
Accurate diagnosis is foundational in oncology. Medical oncologists utilize imaging studies such as CT scans, MRI, and PET scans, along with biopsies and laboratory evaluations. These diagnostic tools allow specialists to assess tumor characteristics, determine cancer staging, and identify molecular markers that guide targeted therapies.
Personalized Treatment Planning
Cancer treatment is highly individualized. A medical oncologist develops personalized plans based on tumor type, stage, patient health, and preferences. Treatments may include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted medical oncologist therapy, and hormone therapy. In some cases, clinical trials provide access to emerging therapies, allowing patients to benefit from the latest advancements.
Integration with Multidisciplinary Teams
Effective cancer care involves collaboration across multiple specialties. A medical oncologist works closely with surgeons, radiation oncologists, pathologists, and palliative care specialists. This coordinated approach ensures that every aspect of patient care is addressed, from precise treatment to supportive therapies that enhance comfort and quality of life.
Managing Treatment Side Effects
Cancer therapies can produce significant side effects, including fatigue, nausea, and immune suppression. A medical oncologist implements strategies to manage these challenges, helping patients maintain physical and emotional well-being. Supportive care may involve medications, dietary adjustments, physical therapy, and counseling services.
Monitoring Response to Therapy
Continuous evaluation is a core aspect of oncology. Medical oncologists track patient response through imaging, laboratory results, and clinical assessment. This ongoing monitoring ensures treatments are effective and allows for timely adjustments if resistance develops or side effects become unmanageable.
Role in Palliative Care
For patients with advanced cancer, a medical oncologist provides palliative care to manage symptoms and maintain quality of life. Palliative interventions focus on pain control, emotional support, and enhancing daily functioning. This care complements curative treatments or serves as the primary focus when disease progression limits therapeutic options.
Patient Education and Engagement
Educating patients is essential in oncology. A medical oncologist ensures patients understand their diagnosis, treatment options, potential side effects, and prognosis. Informed patients are empowered to make decisions aligned with their values and goals, leading to better adherence and improved overall experience.
Advancements in Oncology
Modern oncology benefits from rapid technological and scientific advancements. Medical oncologists integrate precision medicine, genomic profiling, and immunotherapies into treatment plans. Staying updated on emerging research allows specialists to offer innovative solutions and improve long-term patient outcomes.
Long-Term Follow-Up and Survivorship
Post-treatment follow-up is critical. Medical oncologists schedule regular assessments to detect recurrence, monitor late effects of therapy, and support overall health. Survivorship care plans often include lifestyle recommendations, rehabilitation, and psychosocial support to optimize recovery and enhance life after cancer treatment.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Cancer impacts emotional and mental well-being. Medical oncologists collaborate with psychologists, social workers, and support groups to provide comprehensive care. Addressing anxiety, depression, and stress is vital for holistic healing, complementing the physical aspects of treatment.
Conclusion
A medical oncologist is an integral part of modern cancer care, guiding patients through complex treatment journeys with expertise and compassion. Through personalized treatment planning, multidisciplinary collaboration, symptom management, and patient education, these specialists ensure that individuals receive comprehensive care that improves survival and quality of life. From diagnosis to survivorship, the role of a medical oncologist remains central in advancing cancer treatment and supporting patients every step of the way.