Understanding Lie Detector Tests in Utah: How Polygraph Exams Work
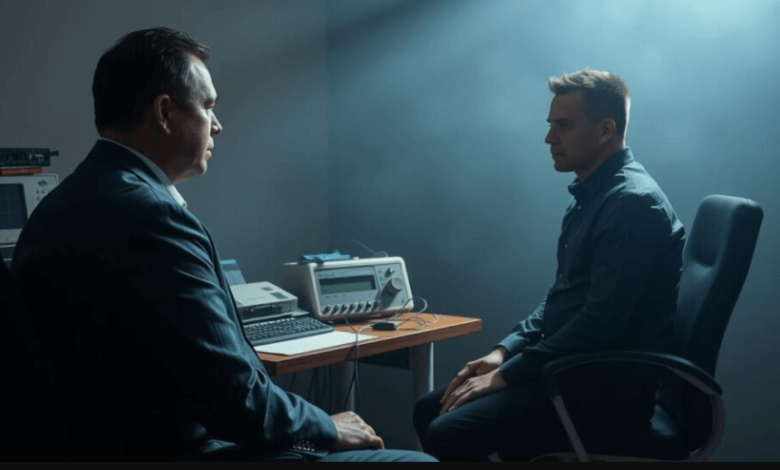

Introduction to Polygraph Tests
A polygraph test, commonly known as a lie detector test, is a technique used to determine whether a person is being truthful or deceptive. It involves monitoring physiological indicators such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and skin conductivity while a subject answers a series of questions. The underlying principle is that deceptive answers will produce physiological responses that can be distinguished from those associated with truthful answers. While polygraph tests are used across various states in the U.S., the legal and practical applications vary widely. In Utah, polygraph exams are commonly used in law enforcement investigations, employment screenings, and even in certain court cases, though their admissibility as evidence in court remains a topic of ongoing debate.
How Polygraph Tests Work
The polygraph machine itself is a sophisticated device equipped with sensors that are attached to a person’s body during the examination. The sensors measure physiological changes that are believed to be associated with the stress or anxiety that may occur when someone is being deceptive. Typically, a test begins with a pre-test interview in which the examiner discusses the questions with the subject to ensure clarity and to establish baseline physiological responses. The questions are then asked in a structured format during the actual exam, usually divided into relevant, irrelevant, and control questions. Relevant questions pertain to the specific issue under investigation, irrelevant questions serve as baselines, and control questions are designed to provoke concern but are not directly related to the case. After the test, the examiner analyzes the results to assess whether the physiological responses suggest truthfulness or deception.
See also: Enhancing Retail Efficiency With Modern Scanning Technology
Polygraph Testing in Utah: Legal and Practical Use
In the state of Utah, polygraph tests are most commonly used by law enforcement agencies during criminal investigations. These tests are typically administered by trained and licensed polygraph examiners, many of whom are certified by organizations such as the American Polygraph Association (APA). Utah does not have state laws that explicitly prohibit or mandate the use of polygraphs, leaving their use largely at the discretion of employers, attorneys, and police departments. In criminal cases, a suspect may be asked to take a polygraph voluntarily, and while the results may help guide an investigation, they are generally not admissible in court unless both the prosecution and defense agree to their use. This is because polygraph results are considered scientifically controversial, with courts questioning their reliability and susceptibility to examiner bias or manipulation by the subject.
Employment and Civil Use of Polygraphs in Utah
Beyond criminal investigations, polygraph tests are also used in Utah for pre-employment screening, particularly in law enforcement and federal government positions. Some private employers may request a polygraph exam for job applicants, but this is subject to strict federal regulation under the Employee Polygraph Protection Act (EPPA). The EPPA prohibits most private employers from using lie detector tests for pre-employment screening or during employment, with exceptions for certain security-related professions or companies handling controlled substances. In civil litigation, polygraphs may occasionally be used as a tool during settlement negotiations or internal investigations, but they rarely serve as definitive proof due to their limitations.
The Debate Over Reliability and Ethical Concerns
Despite their widespread use, polygraph tests remain controversial in both scientific and legal communities. Critics argue that physiological responses to questions can be influenced by a variety of factors, including anxiety, fear, or even medical conditions, none of which necessarily indicate deception. Some individuals can also “beat” the polygraph by employing countermeasures, such as controlled breathing or physical discomfort, to mask physiological responses. Furthermore, the interpretation of polygraph data can be subjective, depending heavily on the skill and objectivity of the examiner. In Utah, as elsewhere, these concerns have led many legal professionals to regard polygraph results as useful investigative tools rather than definitive evidence.
Location in Utah
- Ogden – 298 24th Street, Ogden, UT 84401
Conclusion: The Role of Polygraphs in Utah Today
In summary, while polygraph tests—commonly known as lie detector tests—are a popular tool in Utah for investigations and employment screening, they occupy a complex position in the legal system. Their ability to measure physiological changes is not in dispute, but the assumption that these changes directly correlate with lying remains unproven. As such, their results are often used to support investigative leads rather than as standalone proof of truth or falsehood. For residents of Utah, understanding how polygraph tests work, their legal limitations, and their potential for misuse is essential when encountering these tests in legal or professional settings.